Enneagram Tri-Center 4-6-1: Heart Type 4, Head Type 6, Gut Type 1
The 4-6-1 Tri-Center
-
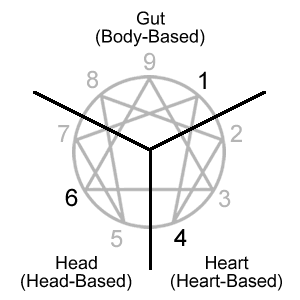
Your tri-center consists of your dominant type in each of the three centers of intelligence with a preferred ordering of the centers (types). The preferred ordering of the 4-6-1 is:
Heart Type: Type 4
-
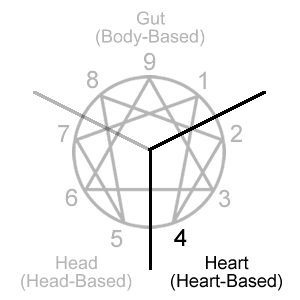
Type 4 is located in the 234 triad which is often described as the heart or heart-based center.
The heart types are focused on interpreting, expressing, and reacting to one’s own emotions or the emotions of others. More specifically, the heart center focuses on what's emotionally significant in the sense that emotions are an indication of how strongly a person resonates with or against something or someone.
This may involve being attentive to the emotional needs and desires of others, seeking emotional affirmation for oneself from others, and expressing one's own unique emotional impression of the world.
Type 4 has emotional impressions of the world which create a rich internal emotional reality. They base their sense of self on this. To express or share this inner emotional world is to share oneself. It can be challenging however to find a way to do this. It can seem like others don't have this same emotional senistivity which can also make the type 4 feel different from other people. This sense of difference can alternate between feeling defective and feeling special.
Type 4 Shame
The shame triad consists of types 2, 3, and 4. Shame for these types involves the heart center. It can be thought of as a feeling of deficiency for not living up to a more idealized sense of self.
This may involve initiating connection with others to avoid feeling unlovable or unimportant in the lives of others, finding value and worth through performance and accomplishment, and finding significance by cultivating and expressing one's uniqueness.
Type 4 shame comes from feeling different from others. It can seem like others are more capable in areas that the type 4 is not. This can sometimes lead to a sense of defectiveness. In compensation, they may search for what makes them uniquely special and try to live from that sense of self instead.
To learn more about Enneagram personality type 4 click here.
Head Type: Type 6
-
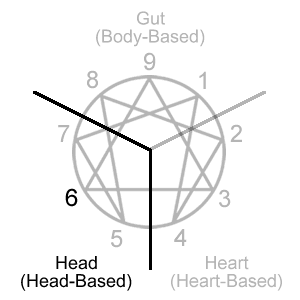
Type 6 is located in the 567 triad which is often described as the head or head-based center.
Although the head types can be thought of in terms of reasoning, analyzing, and other typical thinking functions, a useful distinction from the other two centers can be made in terms of anticipating and preparing for future possibilities.
This may involve gathering data and facts in order to better predict outcomes, preparing for negative potentialities that might occur, and planning or pursuing activities that provide enjoyment and avoid discomfort.
Type 6 thinking often leads to doubts and questioning. This can take place regard one's own thoughts as well as those of others. Some sort of assurance or guidance may be sought in resolving doubts and making decisions. This could come from people, authorities, or systems of thought that over time have shown consistency and been found to be trustworthy and reliable. There can also be a reactionary impulse to jump into action in order to purge any doubts or fears.
Type 6 Fear
The fear triad consists of types 5, 6, and 7. Fear for these types involves the head center. It can be thought of as a negative anticipation of future possibilities and wanting to prepare for or avoid those possibilities.
This may involve learning as much as possible in order to feel competent and knowledgeable, imagining worst-case scenarios and preparing for them, and having alternatives available to avoid being trapped in discomfort or pain.
Type 6 fear can come from imagining worst-case scenarios. This can not only create a cautiousness and seeking of security but also a prepared readiness for the possibility of these scenarios. A general anxiety and sense of doubt about the future and one's own capabilities may be present as well.
To learn more about Enneagram personality type 6 click here.
Gut Type: Type 1
-
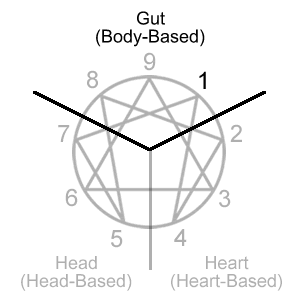
Type 1 is located in the 891 triad which is often described as the gut or body-based center.
There are several ways to interpret what the gut or body types represent. They may be thought of in terms of sensory-somatic (bodily felt sensation), sensory-motor (physical movement and activity), or instinctual (gut decision making).
This may involve taking action based on one's gut instinct, getting pulled along by the agenda of others, and actively trying to correct what's seen as wrong in the world.
Type 1 is often very task-oriented. There can be a lot of activity around organizing, correcting, and improving what seems out of place or doesn't measure up to standards for how things should be. It's hard not to notice when things are not done properly and there is room for improvement. The impulse is to point out to others what needs to be done or correct things themself. This may also involve montoring one's own behavior and that of others.
Type 1 Anger
The anger triad consists of types 8, 9, and 1. Anger for these types involves the gut or body center. It can be thought of as an energy of will that pushes against obstacles to create movement or resists being pushed.
This may involve pushing through obstacles to get what one wants, stubbornly resisting attempts to be pushed in an undesired direction, and getting people to see what's right and correcting things not done right.
Although from the outside type 1 can sometimes appear angry, anger is not usually recognized by the type 1. Instead it takes on other forms such as irritation and criticality, often directed foremost at the self. It's generally felt internally as an energy in service of getting things right or getting others to see what's right. It can sometimes be expressed externally as self-righteous anger or judgment.
To learn more about Enneagram personality type 1 click here.
4-6-1 Tri-Center Focus
-
Expressing-Questioning-CorrectingThe tri-center focus looks at your dominant type in each center through the core focus.
-
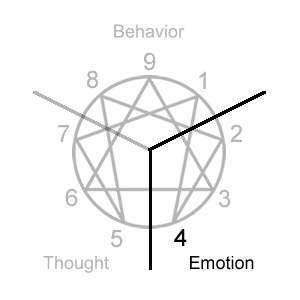
Type 4 Initial Self-Belief: “I am lacking as I am.”
Type 4 Compensation: "I must find and cultivate what's authentic and uniquely special about myself to stand out from the ordinary."
Type 4 Core Focus: Significance comes from cultivating what is unique and emotionally authentic in myself. This requires that I discover and stay true to what has emotional meaning for me and find ways to express that through my own identity and in the world around me.
Personality characteristics that might arise from the type 4 core focus:
- Cultivates and maintains moods they identify with
- Holds in disdain what's common in pursuit of what's special
- Stirs up or intensifies emotional states to feel more alive
- Feels more emotionally sensitive and deeper than others
- Takes things personally even when not intended that way
- Notices what's missing or lacking in self compared to others
- Creates idealized self from what they emotionally resonate with
- Looks for ways to express their inner emotional world
- Wants to deal with internal emotions before moving forward
-
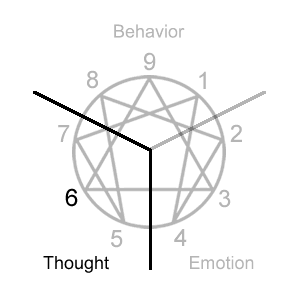
Type 6 Initial Self-Belief: “I am uncertain as I am.”
Type 6 Compensation: "I must search for someone or something that I can depend on that provides the assurance to move forward."
Type 6 Core Focus: Assurance comes from determining what can be trusted so that internal doubts can be resolved. This requires that I find something outside myself that provides support and can be relied upon by questioning the intentions and thoughts of authorities, systems, other people, and even myself.
Personality characteristics that might arise from the type 6 core focus:
- Plays the devil's advocate through contrarian thinking
- Tends to notice what could go wrong in situations
- Mentally prepares for worst-case scenarios
- Becomes suspicious when people behave inconsistently
- Projects imagined thoughts and feelings onto others
- Can be very loyal once someone has earned their trust
- Scans the environment and people for possible threats and danger
- Disarms others through warmth and self-deprecation
- Seeks advice and reassurance when making decisions
-
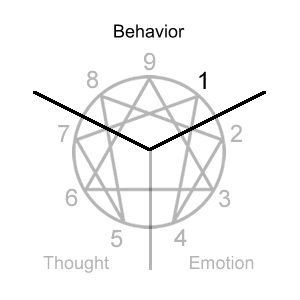
Type 1 Initial Self-Belief: “I am unacceptable as I am.”
Type 1 Compensation: "I must monitor, correct, and improve myself in order to be acceptable and remain above criticism."
Type 1 Core Focus: Acceptability comes from doing things right and acting appropriately according to internalized standards for what that is. This requires I discern what’s right and monitor, correct, and improve my behavior so I don’t fall short of these standards. Others should do the same.
Personality characteristics that might arise from the type 1 core focus:
- Monitors and corrects self-behavior by way of an Inner Critic
- Avoids making mistakes that can be criticized by others
- Compares the world to standards for how things should be
- Tends to look for one right way of doing things
- Strives toward an ideal of perfection
- Attention goes to what needs to be corrected or improved
- Critical of others when they disregard implied rules of behavior
- Tries to be good by modeling appropriate behavior
- Feels responsible for getting things right
Heart Focus: Emotional Authenticity
Type 4 - Significance through Emotional Authenticity
Head Focus: Mental Questioning
Type 6 - Assurance through Mental Questioning
Gut Focus: Behavioral Correctness
Type 1 - Acceptability through Behavioral Correctness
To learn more about the centers and your center types click on a link below.
Enneagram Tests to Help Determine Centers
The Enneagram personality types group the nine types into three centers of intelligence often referred to as the gut, heart, and head centers.
These tests help you find your dominant type in each center and the order of preference for those centers.
-
Dominant Type in Each Center with Wings Test
This test determines your dominant type in each center (aka tri-center, trifix, tritype, truetype) along with the wings of those types.
Use when you want to know your tri-center or tri-center with wings. -
Enneagram Type Preference Test
This test produces a scored list of all nine types.
Questions are forced-choice, similar to the method used by the Riso-Hudson Enneagram Type Indictor (RHETI).
Use to determine type, wings, gut/heart/head types, and tri-center. -
Center Type Comparison Test
This test scores the three types in a given center to determine your dominant type within that center (gut, heart, or head type).
Use when you don't know your dominant type for one of the centers. -
Type Comparison Test
This test compares any two types, producing a score for each.
Use when unsure of your tri-center order or which of two types is preferred for a center.
Click here for the Complete Guide to the Enneagram.
This free guide explains- the nine Enneagram personality types
- the many type variations within type
- where the types came from (origins and history)
- how the types use the Enneagram symbol
Click here for Enneagram tests.
These free tests help you find your- primary type
- candidate types
- preferred wing
- intinctual subtype
- instinctual variant stacking
- center types (gut, heart, and head)
- tri-center with wings