Enneagram Stances / Hornevian Groups: Three coping strategies
While the centers of intelligence describe the set of triads most used with the Enneagram personality types, a lesser known set of triads is often used as well.
Karen Horney's coping strategies
In her book Our Inner Conflicts, written more than two decades before the Enneagram types first appeared, Karen Horney mentioned what she called basic anxiety, which is the feeling a child has of being isolated and helpless in a potentially hostile world. In attempting to cope with this menacing world the child develops not only ad hoc strategies but lasting character trends which become part of personality. She calls these neurotic trends. Here's how she describes the trends in a child's attempt to cope.
When moving toward people he accepts his own helplessness, and in spite of his estrangement and fears tries to win the affection of others and to lean on them. Only in this way can he feel safe with them. If there are dissenting parties in the family, he will attach himself to the most powerful person or group. By complying with them, he gains a feeling of belonging and support which makes him feel less weak and less isolated.
When he moves against people he accepts and takes for granted the hostility around him, and determines, consciously or unconsciously, to fight. He implicitly distrusts the feelings and intentions of others toward himself. He rebels in whatever ways are open to him. He wants to be the stronger and defeat them, partly for his own protection, partly for revenge.
When he moves away from people he wants neither to belong nor to fight, but keeps apart. He feels he has not much in common with them, they do not understand him anyhow. He builds up a world of his own— with nature, with his dolls, his books, his dreams.
In the same book she also described three types of people for which a particular attitude has become predominant and dedicates a chapter to each.
- the compliant type - moving toward people
- the aggressive type - moving against people
- the detached type - moving away from people
The Hornevian groups or triads
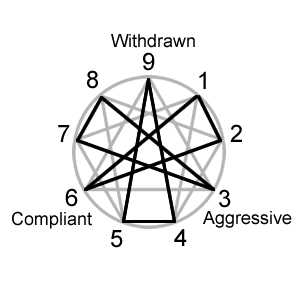
Karen Horney's three types were later placed on the Enneagram personality types by those teaching the Enneagram types. Three triads or groups were created to represent each of Horney's types. The detached type was renamed the withdrawn type in the process. Below is the most common grouping of the types.
- the compliant types: 162
- the aggressive types: 738
- the withdrawn types: 495
Although Karen Horney's descriptions of her types fit for some Enneagram types, they don't actually fit for all the Enneagram types as outlined in the triads. But like many things regarding the Enneagram types, the original descriptions have been adapted to fit the symbol. Each author writing about these triads has their own adaptations or interpretations.
The stances
A more recent interpretation of the Hornevian triads describes them as social stances or social styles. It's presented as how people get what they want (i.e., moving toward, against, or away from other people).
The grouping of the types is the same as the Hornevian triads, but the stances also incorporate an earlier idea about how each triad has a repressed center of intelligence. This is indicated by which center types 6, 3, and 9 are in.
- moving toward other people, repressed head/thinking center: 162
- moving against other people, repressed heart/feeling center: 738
- moving away from other people, repressed gut/doing center: 495
Click here for the Complete Guide to the Enneagram.
This free guide explains- the nine Enneagram personality types
- the many type variations within type
- where the types came from (origins and history)
- how the types use the Enneagram symbol
Click here for Enneagram tests.
These free tests help you find your- primary type
- candidate types
- preferred wing
- intinctual subtype
- instinctual variant stacking
- center types (gut, heart, and head)
- tri-center with wings