Claudio Naranjo's Enneatypes: The Enneagram Meets Psychology
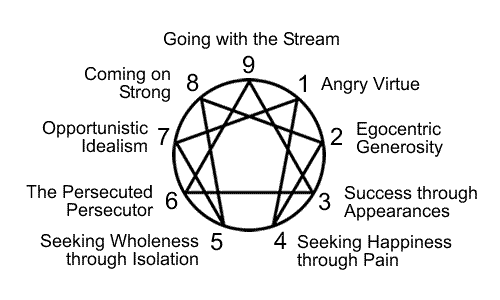
Although the Enneagram personality types find their roots in the work of Oscar Ichazo, it was a psychiatrist named Claudio Naranjo who evolved Oscar Ichazo's ego-types and enneagrams into the personality types we use today (which Naranjo called ennea-types).
Ichazo's enneagrams meet modern psychology
Claudio Naranjo learned of Oscar Ichazo's enneagrams when Naranjo attended a training retreat with others from the United States in Arica, Chile around 1970. The enneagrams were but a small part of the material presented by Ichazo. Ichazo later brought his training to the United States through the Arica Institute in 1971. Naranjo incorporated the enneagrams into his own teachings and evolved the enneagrams along a separate path from Ichazo.

Naranjo expanded upon Ichazo's enneagrams, or ego-types as the five associated enneagrams can be referred to collectively, through his own background in psychology and other understandings. One way he did this was to relate Ichazo's ego-types to the personality disorders of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) used by psychologists. This isn't to say that the Enneagram types are disorders in themselves but that the disorders represent where a type may go when psychologically unhealthy. Mapping the types to the DSM also offered a way to correlate psychological traits with the types, a sort of Rosetta Stone between modern psychology and the Enneagram types.
Things to note about Enneagram type correlations with the personality disorders.
- Naranjo wasn't always consistent with which type he associated with which personality disorder.
- The DSM is not static but has been updated from time to time over the years so the personality disorders have changed over time.
- Other authors and teachers of the Enneagram types may interpret the correlations between the types and the DSM differently from Naranjo and each other.
Naranjo's ennea-types
Naranjo called his version of the Enneagram types "ennea-types" and described them in terms of a trait structure (what follows can be found in his books Ennea-type Structures and Character and Neurosis).
Ennea-type IAngry Virtue - Anger and Perfectionism
- Anger
- Criticality
- Demandingness
- Dominance
- Perfectionism
- Over-Control
- Self-Criticism
- Discipline
Egocentric Generosity - Pride and Histrionism
- Pride
- Love Need
- Hedonism
- Seductiveness
- Assertiveness
- Nurturance and False Abundance
- Histrionism
- Impressionable Emotionality
Success through Appearances - Vanity, Inauthenticity, and the "Marketing Orientation"
- Attention Need and Vanity
- Achieving Orientation
- Social Sophistication and Skill
- Cultivation of Sexual Attractiveness
- Deceit and Image Manipulation
- Other-Directedness
- Pragmatism
- Active Vigilance
- Superficiality
Seeking Happiness through Pain - Envy and the Masochistic Personality
- Envy
- Poor Self-Image
- Focus on Suffering
- "Moving Toward"
- Nurturance
- Emotionality
- Competitive Arrogance
- Refinement
- Artistic Interests
- Strong Superego
Seeking Wholeness through Isolation - Avarice and Pathological Detachment
- Retentiveness
- Not Giving
- Pathological Detachment
- Fear of Engulfment
- Autonomy
- Feelinglessness
- Postponement of Action
- Cognitive Orientation
- Sense of Emptiness
- Guilt
- High Superego
- Negativism
- Hypersensitivity
The Persecuted Persecutor - Fear and Suspiciousness
- Fear, Cowardice and Anxiety
- Over-Alert Hyperintentionality
- Theoretical Orientation
- Ingratiating Friendliness
- Rigidity
- Pugnacity
- Orientation to Authority and Ideals
- Accusation of Self and Others
- Doubt and Ambivalence
Opportunistic Idealism - Gluttony, Fraudulence, and Narcissism
- Gluttony
- Hedonistic Permissiveness
- Rebelliousness
- Lack of Discipline
- Imaginary Wish Fulfillment
- Seductive Pleasingness
- Narcissism
- Persuasiveness
- Fraudulence
Coming on Strong - Lust and Vindictive Arrogance
- Lust
- Punitiveness
- Rebelliousness
- Dominance
- Insensitivity
- Conning and Cynicism
- Exhibitionism (Narcissism)
- Autonomy
- Sensorimotor Dominance
Going with the Stream - Accidia, the Passion for Comfort and the Overadjusted Disposition
- Psychological Inertia
- Over-Adaptation
- Resignation
- Generosity
- Ordinariness
- Robotic Habit-Boundedness
- Distractibility
Most, if not all, people teaching and writing about the Enneagram personality types learned of them directly or indirectly from Naranjo, often adding their own take on the types in the process.
Click here for the Complete Guide to the Enneagram.
This free guide explains- the nine Enneagram personality types
- the many type variations within type
- where the types came from (origins and history)
- how the types use the Enneagram symbol
Click here for Enneagram tests.
These free tests help you find your- primary type
- candidate types
- preferred wing
- intinctual subtype
- instinctual variant stacking
- center types (gut, heart, and head)
- tri-center with wings